APPLIED
EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGYA
SURVEY: THE EFFECT OF EIGHT
WEEKS SUB MAXIMAL PHYSICAL ACTIVITY ON THE PLASMA FIBRINOGEN IN ELDERLY
MALES
Mirdar
Sh1,
Bakhshandeh A1, Sadeghpour B1,
Safiri H21Department
of Exercise Physiology, Faculty of Physical Education and Sport
Sciences, Department of Statistics, Faculty of Basic Sciences,
Mazandaran University, Babolsar, 2Department
of Pathology and Medicine, Babol Medicine Sciences University, Babol,
Mazandaran Province, Iran
The
researches show the risk of catching disease in the inactive persons is
twice as much as active persons. On the other hand, inflammatory
indexes serum measure has considered Fibrinogen, Homocysteine and CRP
in comparison with bloody fats as strong predictors cardio-vascular
occurrences
for researchers. Some of the researchers have reported contrary
relationship between inflammatory indexes and cardio-respiratory
preparedness degrees in the males and females. So, the purpose of
research is the survey the effect of eight weeks sub maximal physical
activity on the plasma. Fibrinogen as cardio-respiratory risk
factors in elderly males.
This periodic re-examination was
the
type of semi-experimental and applied-analytic. The Subjects of the
research be consisted of 3 groups of 21 active middle-aged males
between 50-75 years old that two experiential 1 and 2, and control
groups with Vo2 Peak 51.14±2.7, 52.21±3.23, and
43.61±1.44 (on the basis of 1-mile Track Jog test and were
divided voluntary, the information of standard registered health
questionnaire, Baeck of Habitual Activity, and casually. Experiential
group Ι carried out Balke-Ware sub maximal aerobic exercise 3
sessions and experiential group II, 5 sessions on the week during 8
weeks. But control group didn’t take part in the training
program. Systole and Diastole pressure and heart rate was written by
pulseoximeter any training program. Plasma Fibrinogen was measured by
clot table and chronometric method kit according to mg/dl, before and
after 48 hours training program.
Analysis of results carried
out
paired sample T-Test, One-way ANOVA, multi compare Tukey (LSD) on the
surface of the meaningful P<0.05.
ANOVA Test
| Sum of Squares | df
| Mean
Square | F | Sig.
| Post-VO2 Peak
| Between Groups
| 991.542
| 2
| 495.771
| 13.973
| .000
|
| Within Groups
| 638.657
| 18
| 35.481
|
|
|
| Total
| 1630.199
| 20
|
|
|
| Post-Fibrinogen
| Between Groups
| 3621.429
| 2
| 1810.714
| .542
| .591
|
| Within Groups
| 60128.571
| 18
| 3340.476
|
|
|
| Total
| 63750.000
| 20
|
|
|
|
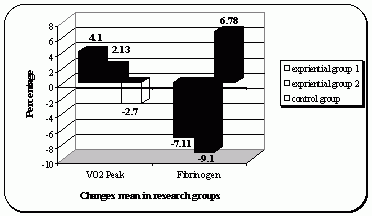
The
result of
research shown Fibrinogen average in the post-test period has decreased
in the two experiential groups, and has increased in the control group,
but these variances weren’t meaningful paired sample T-Test
and
LSD test results. Furthermore, the variances results of Vo2 Peak
average of the research’s subjects had shown increase in the
2
experiential groups and decrease in the control group. Also paired
sample T-Test showed meaningful difference in surface P=0.05 between
Vo2 Peak of all groups. Also results of oneway ANOVA and LSD multiple
comparisons showed meaningful difference after 8 weeks in the sub
maximal aerobic exercise (P=0.001) between Vo2 Peak of experiential and
control groups too.
Generally, the low speed treadmill and
increase of one percent gradient/min was considered two important
elements of Balke-Ware modified protocol, because all subjects would be
carried out 21 stages of 26 stages with out pain and the amplitude of
heart rate 115 to 155 beat/min. In other words, their heart rate would
be balanced in the higher level. So, although Fibrinogen as risk
factors has not shown meaningful variances in the training program, but
meaningful improvement of cardio-respiratory performance is an
expression of the last training program effect for decreasing these
indexes in the experiential group and prevention the incidence of
cardio-vascular probable failures and perhaps appears to need longer
time for more efficacy.
Key
words: sub maximal physical activity, fibrinogen, elderly
male.
|
|

